Here are articles that will help you identify the source of the problem and apply our recommendations:
Diagnosing WiFi connection problems with the WiFiMax app
WiFiMax
You can now access our new self-help app WiFiMax! It helps you diagnose and optimize your Wifi network.
Why WiFiMax?
We recommend using the WiFiMax self-help app if you encounter problems such as:
- Speed issues
- Video buffering
- Wi-Fi coverage issues
- Devices that drop off the network
To get started, download the free WiFiMax app onto your smartphone or tablet from the Apple App Store or Google Play.
How to get started
- Download the app onto your mobile device.
- Select Scan network and wait 2 minutes for the scan to finish.
- Click on Improve network health to diagnose your Wifi.
Here's how it works
The WiFiMax app scans your network and, if it detects a problem, suggests ways to improve your Wifi with easy-to-follow, step-by-step instructions.
The app also generates a unique KEY for each scan session. This identifier will enable our technical support team to see the results if you call us for help.
You still need help?
- You can reach our technical support team at 1-866-967-4266.
- Running an analysis before calling us will speed up troubleshooting. Don't forget to note the unique code at the top left of the screen and communicate it to our technical support agent.
Increase Wi-Fi coverage with range extenders
Why would I need a Wi-Fi range extender?
If you have a large or multi-story home, you may need range extenders to ensure good Wi-Fi coverage in all living areas.
There are several factors that can affect Wi-Fi coverage, but the location of your router is the main thing you need to consider to maximize signal coverage. As a general guideline, you can calculate coverage of about 5 meters (or 20 feet) around your router. Beyond this distance, the signal could be unstable and it would be necessary to use a range extender. Note that it is always possible to add an extender after the initial installation of your equipment.
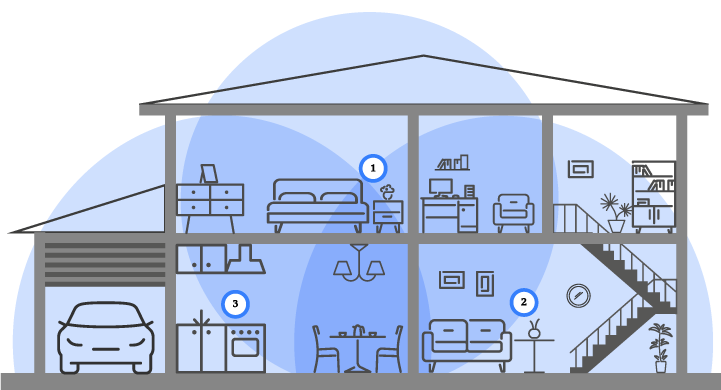
A picture is worth a thousand words!
The following picture shows that using only the Wi-Fi router "1" would give you poor wireless coverage in the garage, the 2nd floor hall, the end of the living room and the entrance.
Using the extender "2" in addition to the Wi-Fi router "1" gives good coverage in the 2nd floor hall, living room and lobby. Adding another extender in "3" gives full coverage to the garage.
Choose according to your needs.
Router only: For single story homes where there is less than 20 feet (5 meters) between the router and devices using Wi-Fi.
Router + 1 extender: For homes with 1 or 2 floors where there is more than 5 meters (20 feet) of distance between the router and devices using Wi-Fi.
Routeur + 2 extenders: I have a large home and I want strong Wi-Fi everywhere, even in the garage!
Oricom's recommendation.
We recommend TP-Link range extenders with OneMesh technology. Get a pre-configured unit from Oricom.

I don't see my Wi-Fi network in the network list
Here are the steps to take when you don't see your Wi-Fi network in the list of available networks.
- Check if the Wi-Fi network is displayed on other devices. If other devices can see and connect to the network, it may indicate a problem with the first device.
- Make sure the router is turned on and plugged in to the correct power supply. (The voltage and amperage on the appliance label should match the voltage and amperage on the power supply label).
- Make sure the Wi-Fi function is enabled on the router. (Some routers have a button to turn Wi-Fi on or off).
- Restart the router. (Unplug the power supply cable and plug it back in after 10 seconds).
Note: Please avoid pressing the "RESET" button on the router, in order to avoid it being restored to its factory configuration. This type of restoration implies that the name of the Wi-Fi network and its password will be changed.
If the problem persists, we invite you to contact technical support at 418 683-4557 or 1 866 967-4266.
How to configure my Wi-Fi network in my router
Here are the steps to configure your wireless network in your router.
- Connect the computer to the Wi-Fi network or to one of the router's " LAN " ports.
- Open your web browser.
- Go to your router's configuration page. The default address for most routers is: 192.168.0.1
- Choose the option for the " wireless " configuration in the menu.
- Enter the name you want to give to your network in the “ wireless network name ” (or “ SSID ”) box.
- Choose " WPA2 " as the security type.
- Enter the password of your choice in the box provided. It is recommended to put numbers, capital letters and special characters for more security.
- Press the button that allows you to save the changes.
Note: For security reasons, it is recommended to change the administrator password of the router for more security.
Slow speed on the Wi-Fi network
Even if you subscribe to an Oricom high speed Internet package, it is possible that one of your Wi-Fi devices or equipment is not making the most of your Internet connection.
To find out if the speed of your Oricom connection corresponds to your package, take our speed test: speed test. If the test results are not as expected, check the following:
- Assess the router environment:
- Make sure the router is in a ventilated area, that it is set up on a table or shelf, and that devices are not stacked.
- Move the router away from devices that cause interference. (Ex: microwave oven, baby monitor, speakers, home cordless telephones).
- Check that the router is plugged in with the correct power supply. (The voltage and amperage on the appliance label should match those on the power supply label).
- Test the speed with a recent device . Some devices from previous generations only support the 2.4GHz frequency band, which is slower and more susceptible to interference than the 5GHz band.
- Turn off or disconnect all other devices to ensure that there is no background bandwidth usage during your test.
- Ideally, connect to the 5GHz network . (The routers configured by Oricom bear the mention 5GHz in the network name (SSID) in order to easily identify them).
- Test the speed while getting close to the router as well as in different places of your home. The Wi-Fi signal degrades with distance and some materials such as concrete or aluminum can reduce the Wi-Fi signal. If necessary, a better performing router or Wi-Fi repeater could improve the range and signal coverage.
- Change the Wi-Fi channel ("channel"). If there is a lot of interference, another channel may provide better results. It is possible to change it from the router's configuration page.
- If you have several routers or signal repeaters, you must disconnect from the repeater with a weak signal in order to be able to connect to equipment with a stronger signal.
- Test with a different device. Performance may vary from device to device.
- Restart the router . (Unplug the power supply cable and plug it back in after 10 seconds).
To better understand Wi-Fi technology, you can read the article: Wi-Fi 101. If the problem persists, you can contact technical support at 1-866-967-4266.
Loss of connection to the Wi-Fi network
Disconnections from the Wi-Fi network can have different explanations. On this page you will find the main causes and possible solutions.
The router environment
- Make sure the router is in a ventilated area, placed on a table or shelf, and that devices are not stacked.
- Move the router away from devices that cause interference. (Ex: microwave oven, baby monitor, speakers, home cordless telephones).
- Check that the router is plugged in with the correct power supply. (The voltage and amperage on the appliance label should match those on the power supply label).
Signal strength and range
The Wi-Fi signal deteriorates with distance, and it may not be strong enough in different places in your home. In some situations, the router is not enough to cover the entire home.
- Check the strength of the wireless signal by clicking on the icon in the lower right corner of your screen. In the example, the "your SSID" network has a signal at full capacity.
- Among the free solutions to a weak signal, you can:
- Move the device to get a better signal
- Move the router to change its coverage
- Remove sources of interference and obstacles between the router and the device
- Sometimes moving devices is not an option. In this situation, the solution is to get one or more devices to increase the Wi-Fi coverage:
- Wi-Fi repeaters - These are used to rebroadcast the Wi-Fi signal from your home router. The main downside is that your devices won't automatically switch between Wi-Fi broadcasts and you will experience disconnection during a manual switchover.
- Mesh Wi-Fi - It uses multiple nodes to create one large, continuous Wi-Fi network that covers your entire home. Your devices automatically and continuously connect to the nearest node as you move around your home. This solution is generally more expensive.
Comparison of devices used to increase Wi-Fi coverage
Wi-Fi 101
Wi-Fi is part of our daily life. It allows us to use Internet connections from various smart devices. This technology uses radio signals of a certain frequency to communicate with our devices and connect them to the Internet without having to go through a wired connection.
There are many factors that can affect the speed of your Internet connection, including:
- The speed of the website you are downloading information from (unfortunately we have no control over this)
- The devices used to connect
- Sources of interference
- The frequency band you are connected to (2.4GHz or 5GHz)
- Signal coverage
- Bandwidth usage
The devices used
You have probably noticed that not all of your equipment offers the same performance. Each device has a Wi-Fi standard that represents the maximum speed that the device can achieve.
Older equipment, such as smartphones and tablets from previous generations, will experience slower speeds. In some cases, equipment can only connect to the 2.4GHz frequency band which is slower and more susceptible to interference than the 5GHz band.
Sources of interference
Some building materials and other objects between your router and your mobile devices can affect signal strength, either because they cause interference or because they obstruct it. If possible, try to use your device with a clear view of your router.
There may be signal interference due to traffic on your wireless network, your neighbors' Wi-Fi network, or other sources of interference.
2.4GHz vs 5GHz
It is possible to connect to a 5GHz or 2.4GHz frequency band. Some older devices can only connect to the 2.4GHz band.
Frequency band affects sensitivity to interference, signal range and performance.
Sensitivity to interference :
A 5 GHz network is less likely to have interference problems because many devices such as Bluetooth® devices, cordless phones, microphones waves, and computers use the frequency of 2.4 GHz.
Range :
The 5 GHz band has a shorter range which allows a shorter distance to be covered than with the 2.4 GHz band.
Signal performance :
The 5GHz band uses shorter radio waves, which provides better speed and stability.
Applications :
The 2.4 GHz band is suitable for easy navigation and for sending emails. These apps don't take up too much bandwidth and perform well at a greater distance.
The 5 GHz band has a wider wireless spectrum, resulting in more meaningful performance. This is why the 5GHz band is recommended for streaming media and transferring music, photos, and videos.
Signal coverage and range
Wi-Fi repeater and Mesh Wi-Fi Network
In some situations, a single router is not enough to cover the entire home. Some devices can be purchased to increase Wi-Fi coverage. Wi-Fi repeaters and Wi-Fi Mesh can both improve signal coverage in your home.
Mesh Wi-Fi uses multiple nodes to create a single, large, continuous Wi-Fi network that covers your entire home. Your devices automatically and continuously connect to the nearest node as you move around your home.
Bandwidth usage
Speed drops are possible if your plan is not sufficient for your needs or if several users are using your Internet access simultaneously.
Some of the devices connected to the Wi-Fi network may also be using Internet access in the background.
Here are some examples of background bandwidth usage:
- Operating system update
- Smart TV software update
- Updating applications
- Synchronization of photo albums
- Online hosting (Cloud)
Some Internet services require more bandwidth than others. Here are some approximate usage examples of some Internet services:
If our articles were not able to resolve your connection issue, or if you require assistance, please do not hesitate to contact Technical Support at 418 683-4557 or 1 866 967-4266.




